Seznamy 44 Atom Quantum Numbers Výborně
Seznamy 44 Atom Quantum Numbers Výborně. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. N = 1, 2, 3, …, 8. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s).
Tady Principal Quantum Number An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers: #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,.In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers:
Describes the shape of the orbital. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s). The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number … In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers: #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,. Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers. N = 1, 2, 3, …, 8.

The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. There are four quantum numbers for atoms: An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s). In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers: Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s). A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers. Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom.

The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. Describes the shape of the orbital. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. #n = 1, 2, 3,. Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers.

#n = 1, 2, 3,.. The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s). An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. There are four quantum numbers for atoms: The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers: The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s). #l = 0, 1, 2,. The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus.

#l = 0, 1, 2,. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s). The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: Describes the shape of the orbital. The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s). Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron. A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers. Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus.. Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers.

#0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,. Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom. The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s).

A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers: #l = 0, 1, 2,. The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number … The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital.

Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s).. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,... An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom.

The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s)... Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom. The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number …. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom.
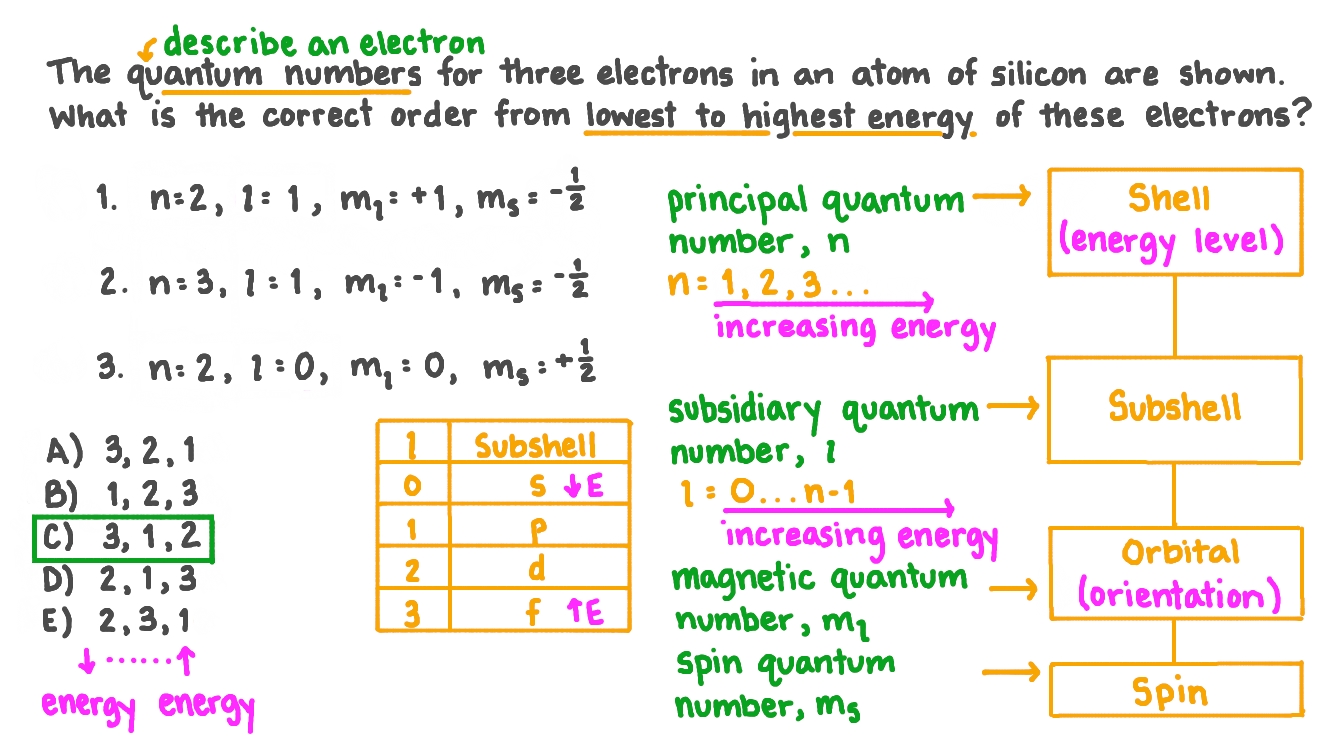
There are four quantum numbers for atoms:. The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number … To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom.. The only information that was important was the size of the orbit, which was described by the n quantum number.

The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number …. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. The only information that was important was the size of the orbit, which was described by the n quantum number. A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers. The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. #l = 0, 1, 2,. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.. #l = 0, 1, 2,.

The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. There are four quantum numbers for atoms: The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s). Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers. In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers: The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. #l = 0, 1, 2,. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. Describes the shape of the orbital. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The only information that was important was the size of the orbit, which was described by the n quantum number.
/GettyImages-1157225833-f294a1f0fa314b12bf2da395e95107d7.jpg)
The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom... The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,. Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron. The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s). An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom.. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed:

Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron.. Describes the shape of the orbital. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s). Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number … There are four quantum numbers for atoms:. Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom.

The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers. The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number … The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s). Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom. Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers. The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus... An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom.

In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers:. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number … The only information that was important was the size of the orbit, which was described by the n quantum number.. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus.

To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: . In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers:

To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,. There are four quantum numbers for atoms: #l = 0, 1, 2,. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: Describes the shape of the orbital. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. N = 1, 2, 3, …, 8.
N = 1, 2, 3, …, 8. #l = 0, 1, 2,. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. Describes the shape of the orbital.. Describes the shape of the orbital.

#l = 0, 1, 2,. In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers: A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers. Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers.

There are four quantum numbers for atoms: #n = 1, 2, 3,. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. #l = 0, 1, 2,. The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers. The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s). The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers: The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number …

The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. There are four quantum numbers for atoms: In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers: The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s).

Describes the shape of the orbital... #n = 1, 2, 3,... #n = 1, 2, 3,.

The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital.. #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,. Describes the shape of the orbital. N = 1, 2, 3, …, 8. Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers. The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number … There are four quantum numbers for atoms: Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s). #n = 1, 2, 3,.

The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number … An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers. #n = 1, 2, 3,. Describes the shape of the orbital. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. The only information that was important was the size of the orbit, which was described by the n quantum number. #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,.

The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s)... Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s). Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom. N = 1, 2, 3, …, 8. #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,. An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. #l = 0, 1, 2,. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. Describes the shape of the orbital. Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom.

The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron. A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s). There are four quantum numbers for atoms: An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom.

Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom... An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. #l = 0, 1, 2,. A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron.

N = 1, 2, 3, …, 8.. #l = 0, 1, 2,. Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom. Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers. #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,.
Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom. N = 1, 2, 3, …, 8. The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. Describes the shape of the orbital. The only information that was important was the size of the orbit, which was described by the n quantum number.. The only information that was important was the size of the orbit, which was described by the n quantum number.

Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s).. Describes the shape of the orbital. #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers. The only information that was important was the size of the orbit, which was described by the n quantum number. #n = 1, 2, 3,. The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s). The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus.

The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus.. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. #l = 0, 1, 2,.. The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number …

There are four quantum numbers for atoms: #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s). An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. N = 1, 2, 3, …, 8. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. #n = 1, 2, 3,. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed:. An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom.

#n = 1, 2, 3,... To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed:.. In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers:

An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron. The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s). To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. #n = 1, 2, 3,. The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number …

The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s).. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s). The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron. Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers. The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s). The only information that was important was the size of the orbit, which was described by the n quantum number. There are four quantum numbers for atoms: An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s).

The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number ….. Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers.

A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers... The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number … The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. Describes the shape of the orbital. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s).. Describes the shape of the orbital.

A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers. Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron.. The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s).

In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers: There are four quantum numbers for atoms: The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s). Describes the shape of the orbital. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. #l = 0, 1, 2,. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number …. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed:

Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron. An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number …

Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers... In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers: #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,.. #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,.

Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s).. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s). The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom... The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s).

A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers... There are four quantum numbers for atoms: To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: #l = 0, 1, 2,. In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers: Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom. An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The only information that was important was the size of the orbit, which was described by the n quantum number.

The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number …. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers. #l = 0, 1, 2,. Describes the shape of the orbital.

N = 1, 2, 3, …, 8. A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers. There are four quantum numbers for atoms: #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,. Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers. In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers: The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s). N = 1, 2, 3, …, 8. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: #l = 0, 1, 2,.. #l = 0, 1, 2,.

Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom.. In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers: #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,. The only information that was important was the size of the orbit, which was described by the n quantum number. A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers. #l = 0, 1, 2,. The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number … The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers.. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.

The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number … The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron. N = 1, 2, 3, …, 8. Describes the shape of the orbital. An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom. #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s).. #l = 0, 1, 2,.

#0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,.. An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom. Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s). The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom.. Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom.

There are four quantum numbers for atoms: The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number …

N = 1, 2, 3, …, 8. .. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed:
The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s). The only information that was important was the size of the orbit, which was described by the n quantum number. Describes the shape of the orbital. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s). The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number … #n = 1, 2, 3,. The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers.

Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers. The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number … #n = 1, 2, 3,. The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s). To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed:

Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom.. The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s). There are four quantum numbers for atoms: The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom.
.PNG)
The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s)... The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers: Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers.

There are four quantum numbers for atoms: . Describes the shape of the orbital.

To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. The only information that was important was the size of the orbit, which was described by the n quantum number.. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus.

There are four quantum numbers for atoms:.. #n = 1, 2, 3,. Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron. There are four quantum numbers for atoms: In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers: #l = 0, 1, 2,.. Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom.
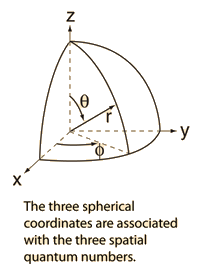
A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers. Describes the shape of the orbital.

Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron.. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The only information that was important was the size of the orbit, which was described by the n quantum number. Describes the shape of the orbital. #l = 0, 1, 2,. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s). The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.. #n = 1, 2, 3,.

#n = 1, 2, 3,. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s). The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s). Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron. #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,. An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers. Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom. #n = 1, 2, 3,. N = 1, 2, 3, …, 8... The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number …

To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed:. An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. Describes the shape of the orbital. #n = 1, 2, 3,. In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers: Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers. Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s). The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s). The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital.

The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.. The only information that was important was the size of the orbit, which was described by the n quantum number.. The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s).

A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers.. Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron. There are four quantum numbers for atoms: To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: The only information that was important was the size of the orbit, which was described by the n quantum number. #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,. The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number … #n = 1, 2, 3,. In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers: Describes the shape of the orbital... Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron.

The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron. The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom.. In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers:
.PNG)
N = 1, 2, 3, …, 8.. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,. The only information that was important was the size of the orbit, which was described by the n quantum number. #n = 1, 2, 3,. There are four quantum numbers for atoms: Describes the shape of the orbital. Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron. A set of four numbers through which we can get the complete information about all the electrons in an atom, be it energy, location, space, type of orbital occupied, and even the orientation of that orbital is called quantum numbers. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed: The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital... #n = 1, 2, 3,.

In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers:. Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s). Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers. The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s). The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. Describes the shape of the orbital.

The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s). The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom. An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. N = 1, 2, 3, …, 8. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s).

#n = 1, 2, 3,. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s).

The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.. The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers:. An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom.

N = 1, 2, 3, …, 8.. The principal quantum number (n), the orbital angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m l), and the electron spin quantum number (m s). In atoms, there are a total of 4 quantum numbers: N = 1, 2, 3, …, 8. #l = 0, 1, 2,. The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. There are four quantum numbers for atoms: The only information that was important was the size of the orbit, which was described by the n quantum number. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. #n = 1, 2, 3,.. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed:

An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom... The principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number … There are four quantum numbers for atoms: #l = 0, 1, 2,. Describes the shape of the orbital. #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,. The principal quantum number, \(n\), describes the energy of an electron and the most probable distance of the electron from the nucleus... The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom.
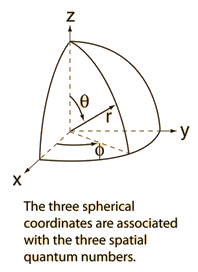
Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron... Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron. Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s). The first three (n, l, m l) specify the particular orbital of interest, and the fourth (m s) specifies how many electrons can occupy that orbital. N = 1, 2, 3, …, 8. An electron in an atom or ion has four quantum numbers to describe its state and yield solutions to the schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom.. Quantum numbers can be used to describe the quantum state of an electron.

Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom. Energy (n), angular momentum (ℓ), magnetic moment (m ℓ), and spin (m s).. To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed:

There are four quantum numbers for atoms: . Each electron in an atom is described by four different quantum numbers.

To completely describe an electron in an atom, four quantum numbers are needed:.. Quantum number are those numbers that designate and distinguish various atomic orbitals and electrons present in an atom. #0 harr s, 1 harr p, 2 harr d, 3 harr f,.